Project Description
This Active Directory lab project demonstrates the setup and configuration of a complete Windows Server environment with Active Directory Domain Services. The lab environment simulates a real-world enterprise network infrastructure, providing hands-on experience with domain controllers, user management, group policies, and network security.
The project encompasses the full lifecycle of Active Directory implementation, from initial server setup through advanced configuration and security hardening. This comprehensive approach provides practical experience with enterprise directory services that are fundamental to modern IT infrastructure.
Objectives
- Deploy and configure Windows Server with Active Directory Domain Services
- Implement domain controller functionality and DNS integration
- Create and manage organizational units, users, and groups
- Configure Group Policy Objects for centralized management
- Establish secure network communication and authentication
- Implement security best practices and access controls
Platforms and Tools Used
- VMware Workstation Pro - Virtualization platform
- Windows Server 2019/2022 - Domain controller operating system
- Windows 10/11 - Client workstation operating systems
- Active Directory Domain Services - Directory services role
- DNS Server - Name resolution services
- Group Policy Management Console - Policy configuration tool
- PowerShell - Automation and management scripting
Step-by-Step Process
Step 1: Prepped for Domain Controller
Process: Deployed a Windows Server 2022 VM using UTM on a MacBook Pro. Installed the OS and completed the basic configuration. Performed initial server updates and renamed the machine to DC1 to act as the primary domain controller.
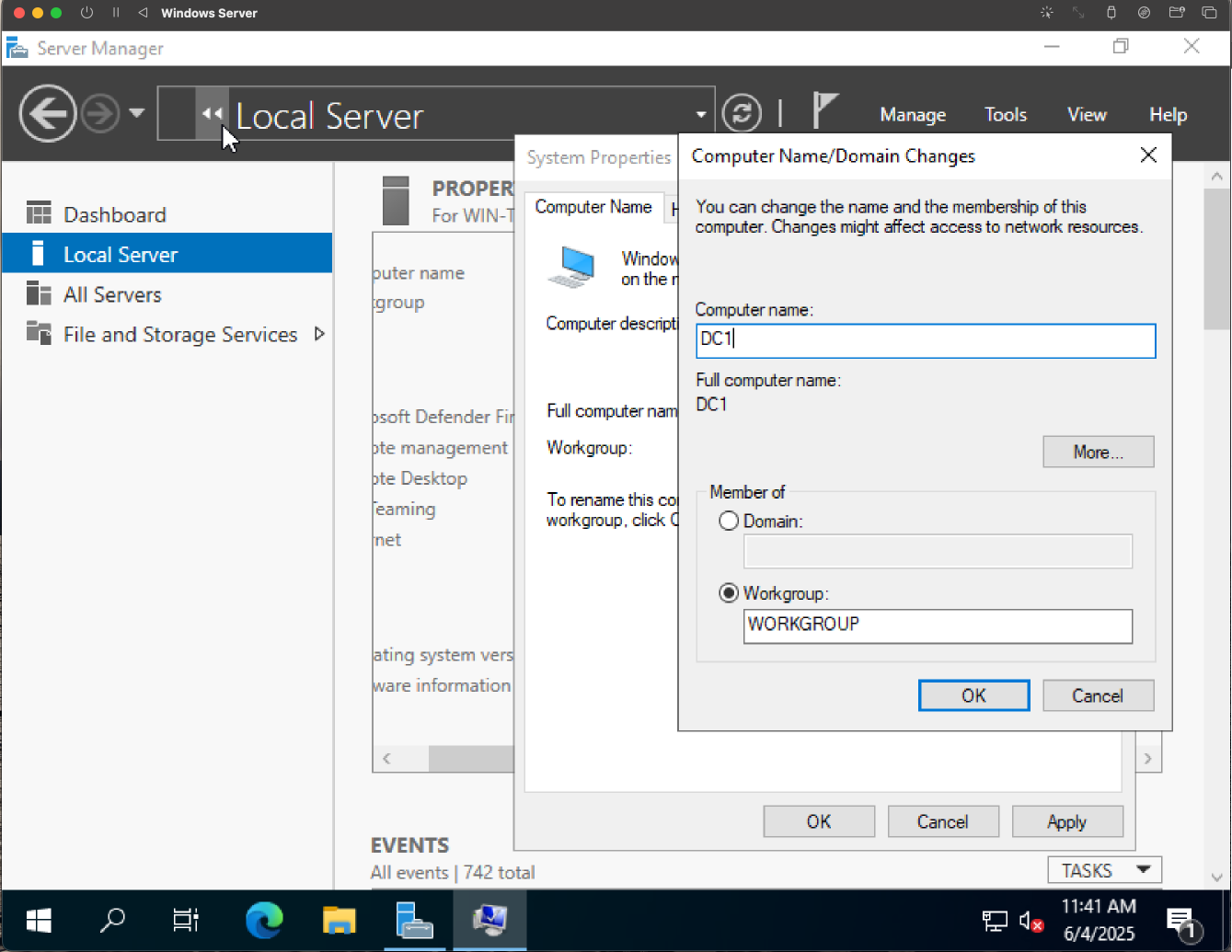
Purpose: Renaming the server gives us a clear hostname that reflects its role in the network. Leaving the server with a default name can make network management and troubleshooting a hassle.
Step 2: Configure Static IP Address on DC1
Process: Configured a static IP and DNS address via the server's network adapter settings to ensure consistent domain resolution. Set the DNS to point to the server's own IP for internal name resolution.
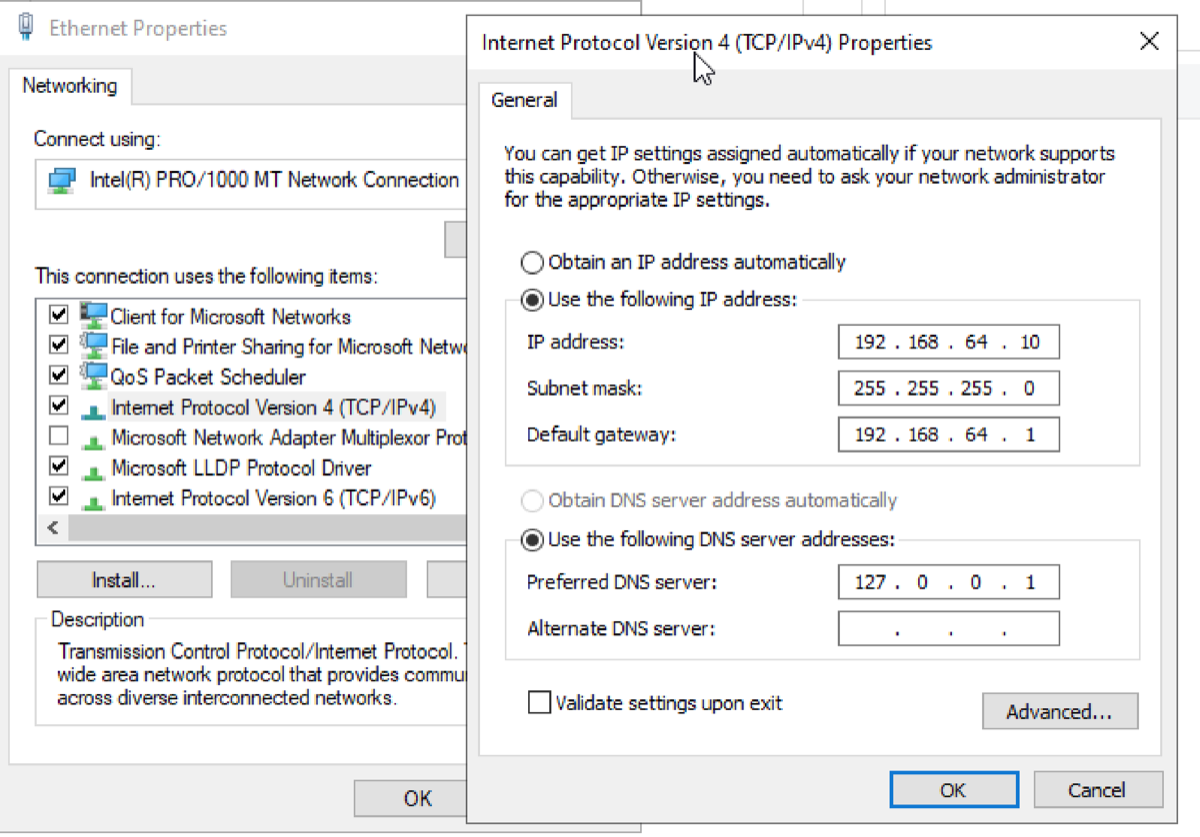
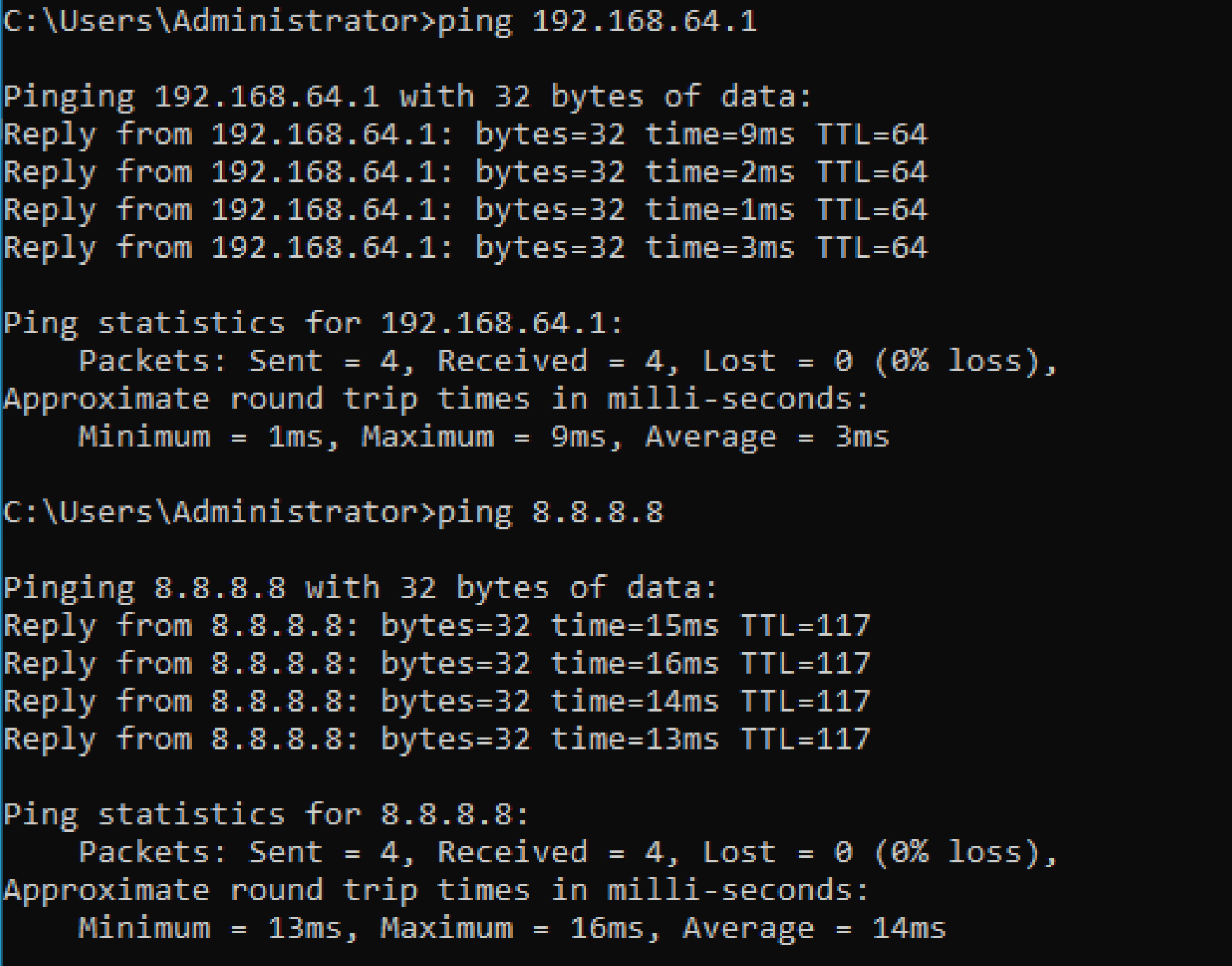
Purpose: A Domain controller must have a fixed IP address to reliably provide services like DNS and Active Directory. Here, I manually set a static IP based on my current network range. A ping test was used to confirm the IP and gateway worked correctly.
Step 3: Install Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS)
Process: Installed the Active Directory Domain Services role on the server in preparation for domain controller promotion.
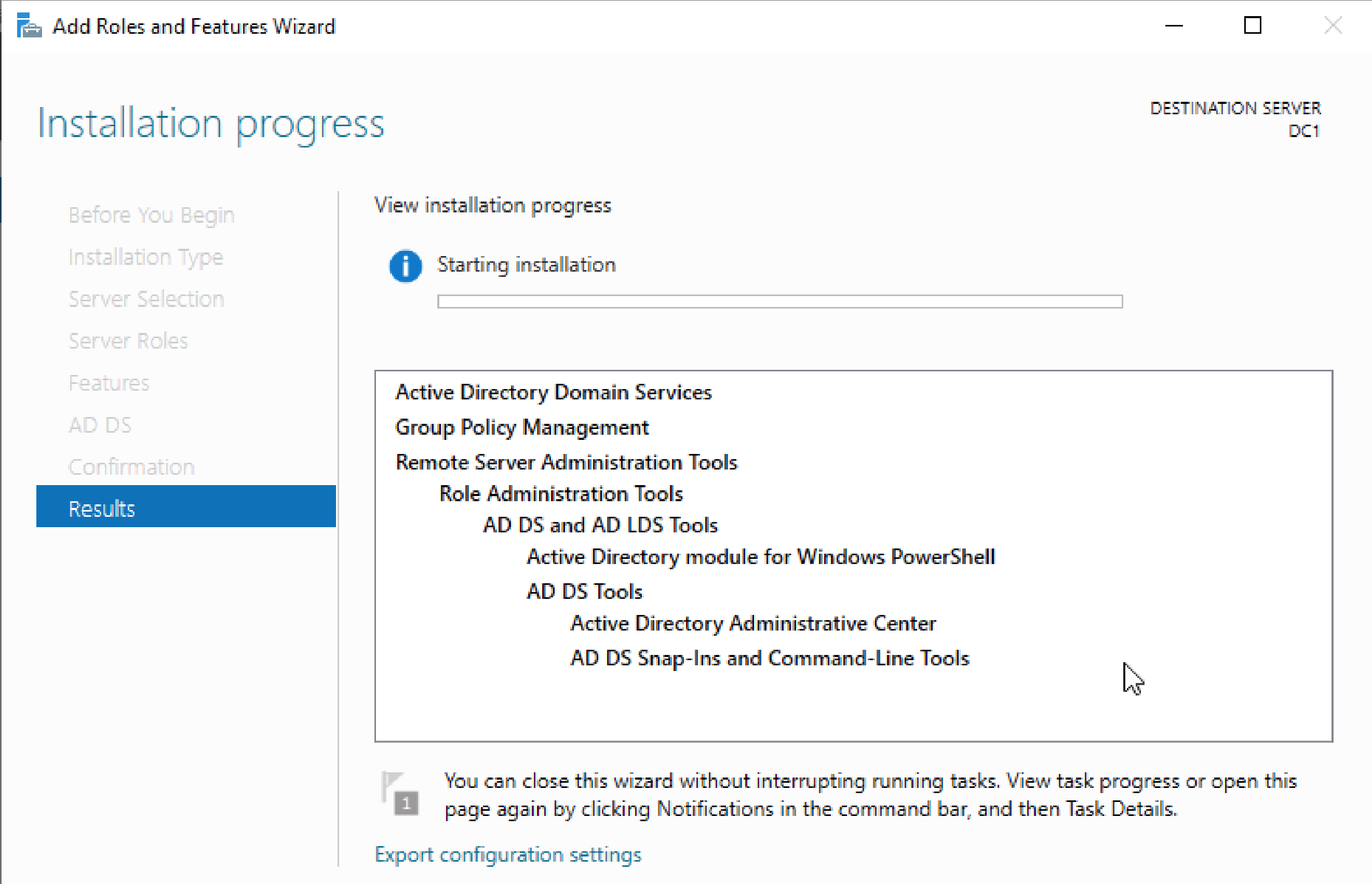
Purpose: AD DS is required for creating and managing domains, users, security groups, and other policies. This prepares DC1 to be the first domain controller in my lab network.
Step 4: Promote Server to Domain Controller
Process: Promoted the server to a domain controller for the newly created forest plaines.local. Set a Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) password and rebooted to complete configuration.
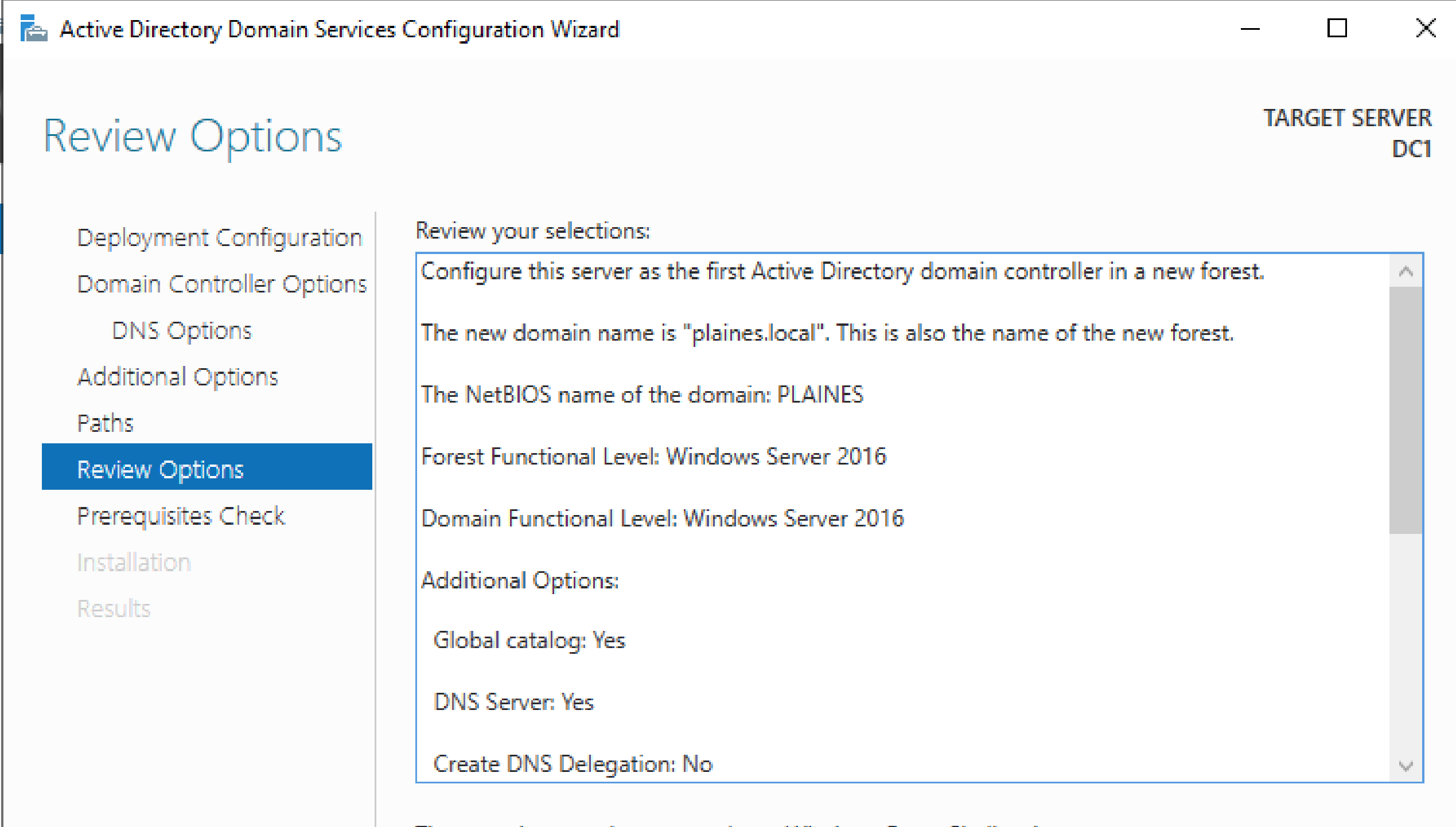
Purpose: This step promoted DC1 to an actual domain controller and created the plaines.local AD forest. It also installed and configured the DNS, Global Catalog, and directory partitions.
Step 5: Create OU - LabUsers
Process: Created an Organizational Unit (OU) named LabUsers to logically separate users and devices. Moved the Lab User machine into the appropriate OU.
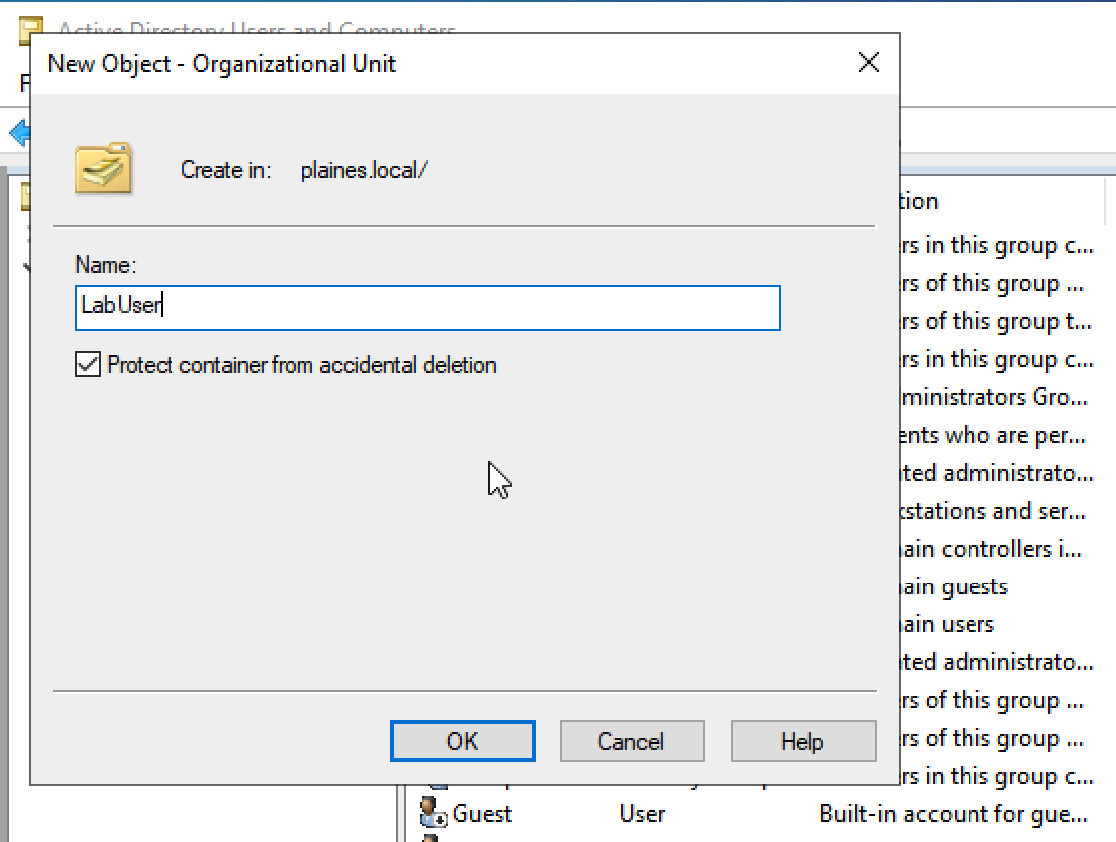
Purpose: OUs provide structure in Active Directory. They allow for more granular management of users, computers, and policies. This OU was created to isolate all lab client machines for testing.
Step 6: Create Domain User
Process: Created a standard domain user (Lab User) in Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) to simulate a non-privileged user. This account was used for later policy enforcement testing.
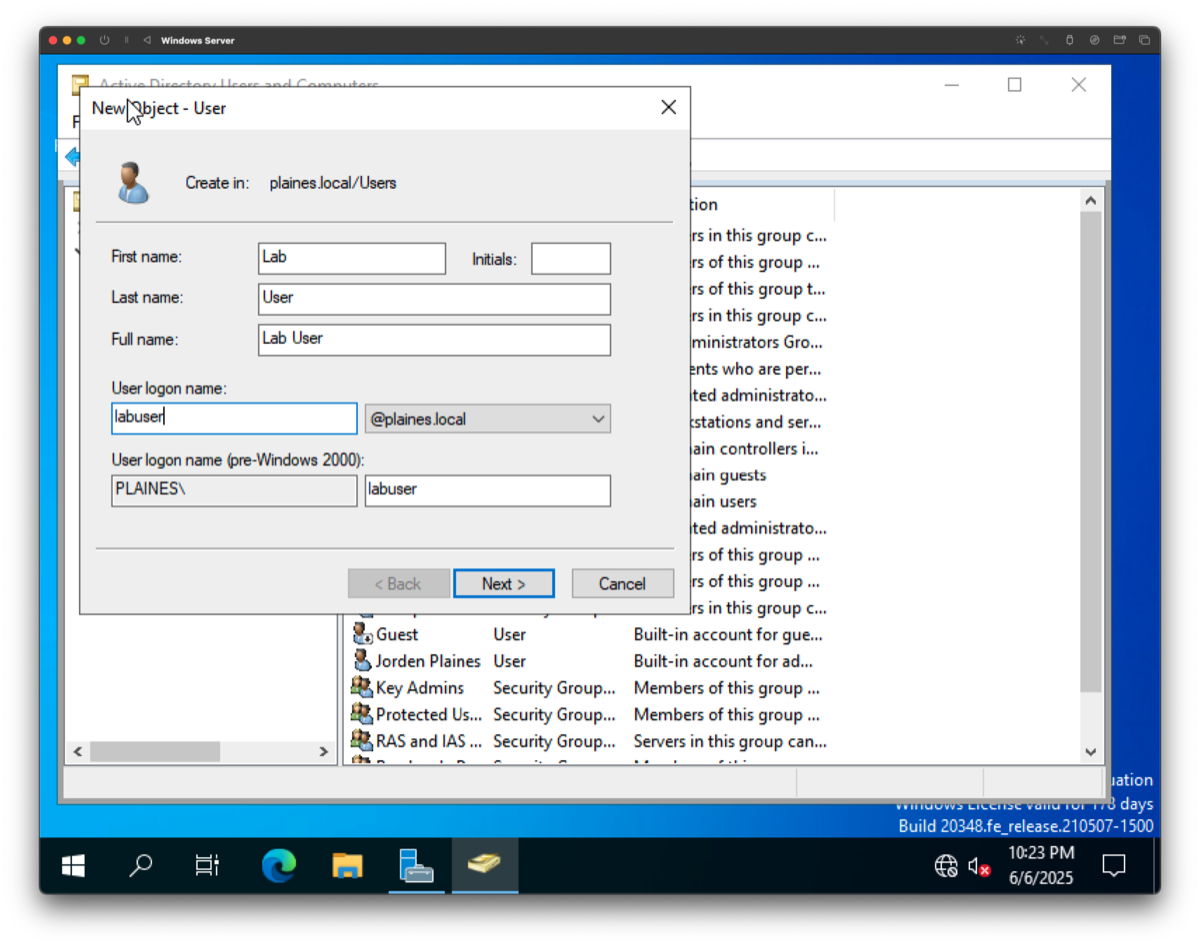
Purpose: Creating a test domain user allows us to validate domain join and user-level permissions from a Windows 11 client system.
Step 7: Join Client to Domain & Log In
Process: On a Windows 11 VM running in Parallels (Mac Mini), configured a static IP and DNS, renamed the computer, and joined it to the plaines.local domain. Restarted and verified domain connectivity.
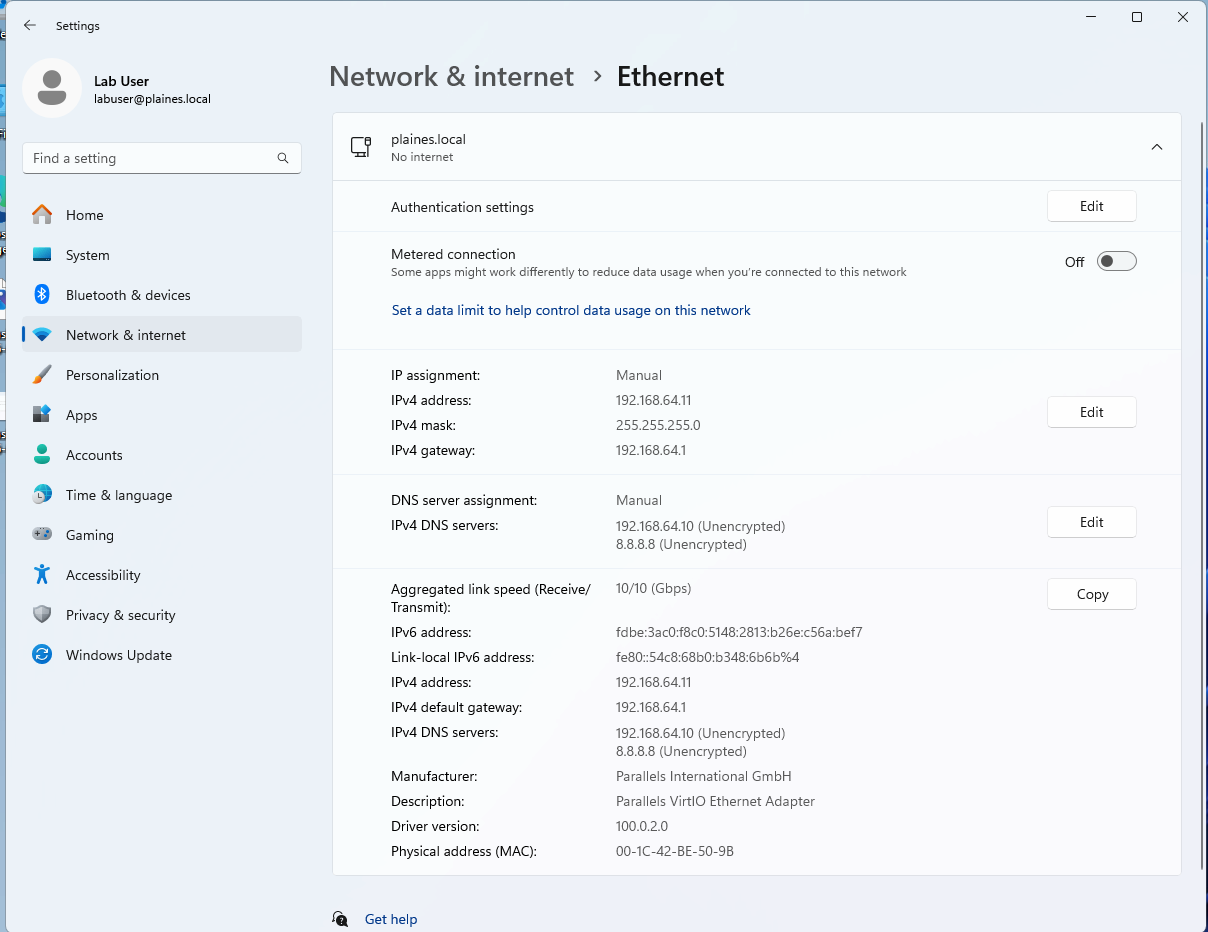
Purpose: The goal was to enable the client to communicate with the DC and become a domain-joined device, allowing centralized management through Active Directory.
Step 8: Move Domain-Joined Client to LabUsers OU
Process: Moved the Windows 11 client into the LabUsers OU in preparation for Group Policy application.
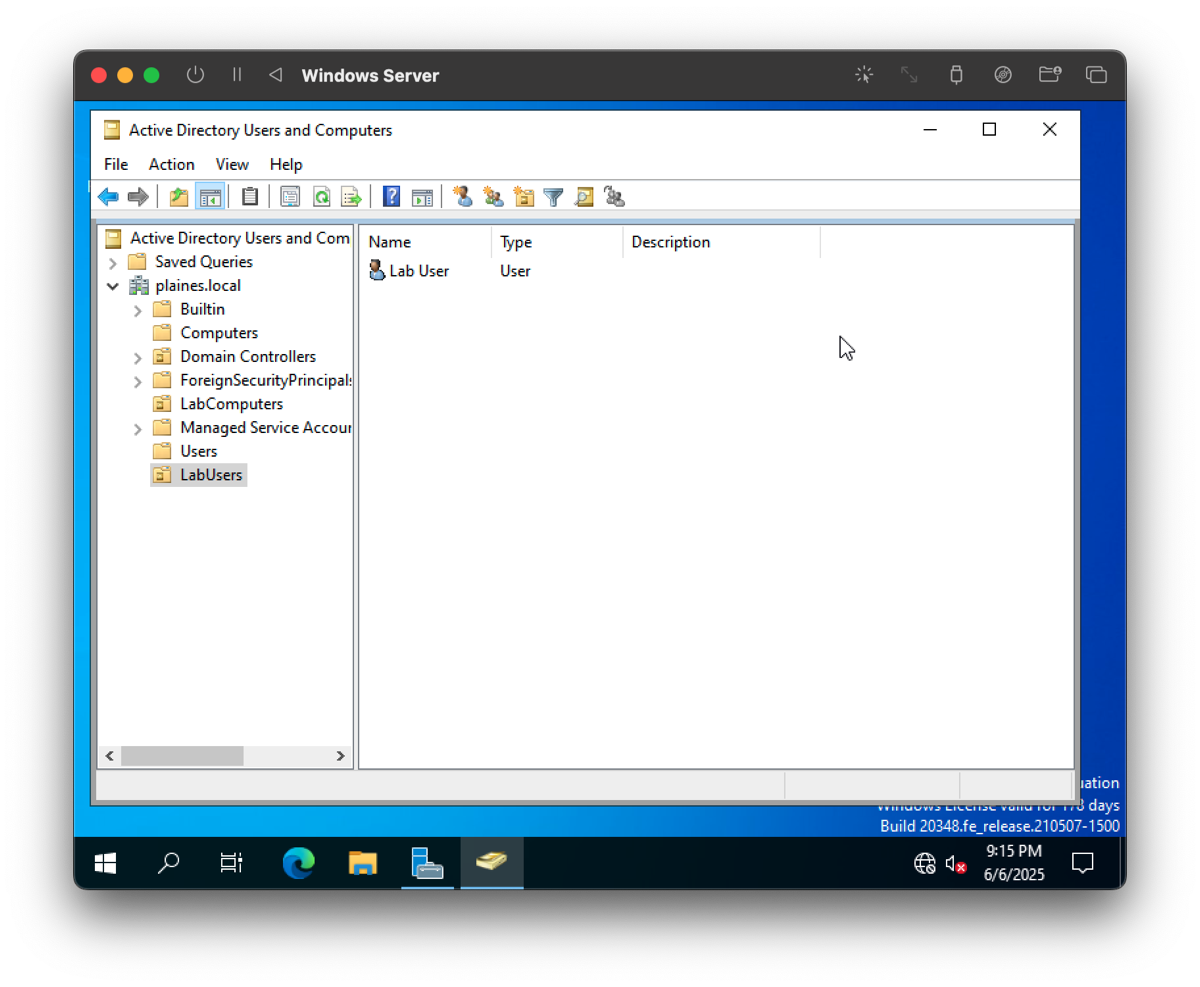
Purpose: Organizing client machines under the appropriate OU allows for scoped GPO application targeting specific sets of machines.
Applied Security Policies:
- Control Panel and PC Settings Access Disabled: Restricts users from modifying system configurations or personalization options.
- Registry Editing Tools Access Blocked: Prevents unauthorized alterations to critical registry settings.
Silent execution of regedit is specifically disabled: Enabled. - Command Prompt Access Restricted: Blocks users from running commands that could impact system stability or security.
Step 9: Create and Link a GPO to the LabUsers OU
Process: Used Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) to create a GPO titled "LabUsers - Basic Restrictions" and linked it to the LabUsers OU to begin applying user-based policies.
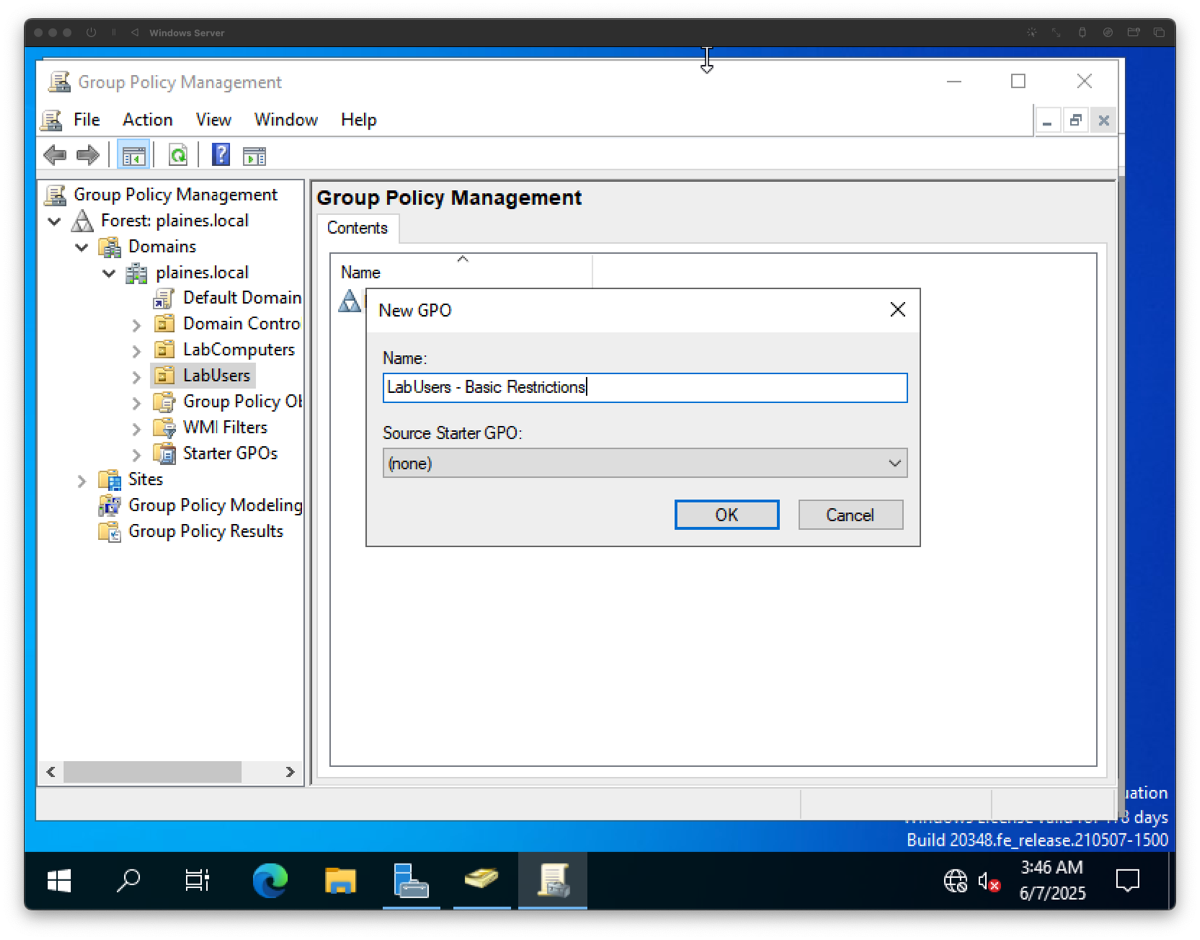
Purpose: Linking the GPO allows custom restrictions to apply to standard domain users. This step enforces basic security policies such as disabling access to the Control Panel, Command Prompt, and registry tools.
Step 10: Configure LabUsers GPO
Process: Edited the GPO to disable access to the Control Panel, Registry Editor, and Command Prompt under User Configuration > Administrative Templates. Verified GPO application by logging in as Lab User.
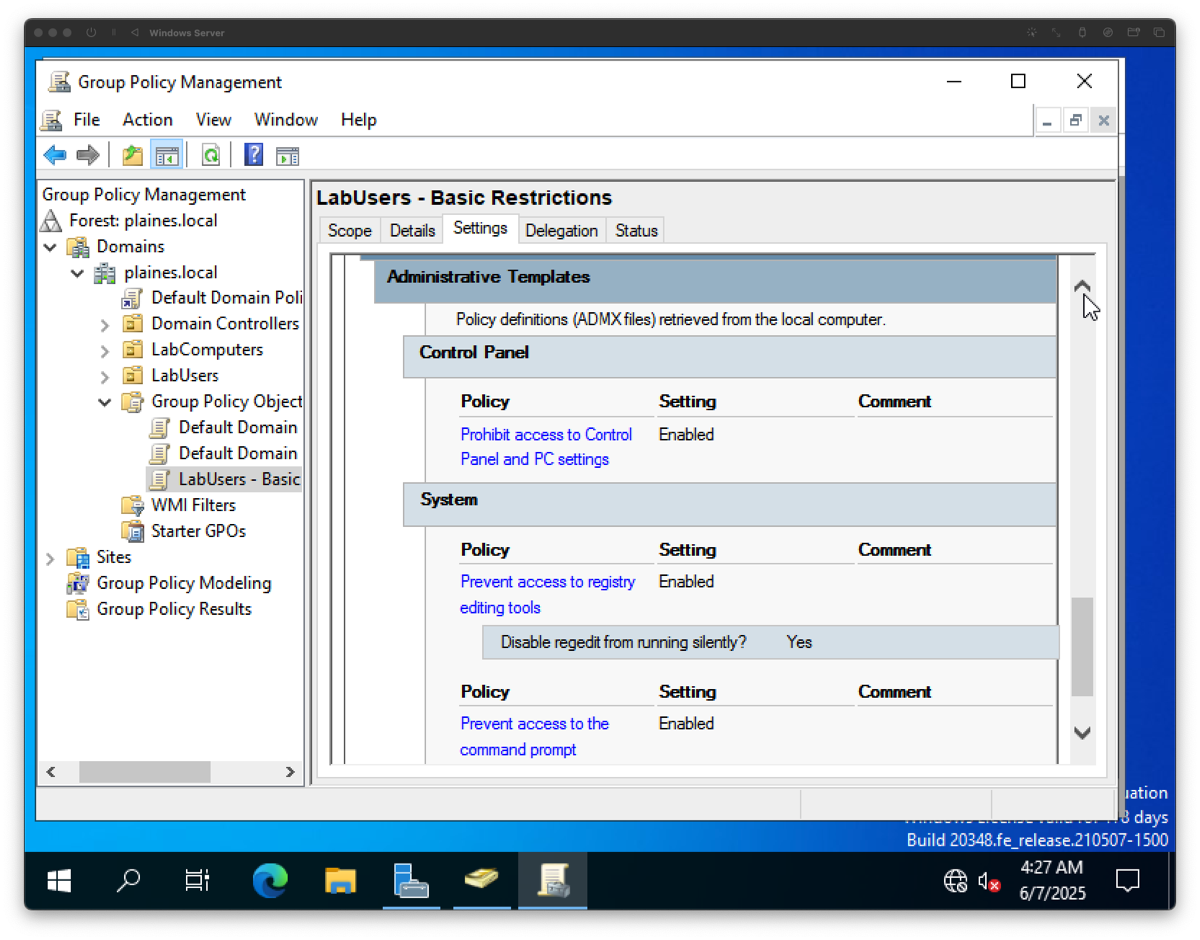
Purpose: These restrictions enforce a locked-down environment for standard users. Policies such as disabling regedit, CMD, and Control Panel reflect real-world enterprise policy enforcement.
Step 11: Test GPO Enforcement
Process: Logged into the domain-joined client as Lab User and tested the GPO configuration. Verified that access to the Control Panel, Registry Editor, and Command Prompt was restricted as intended.
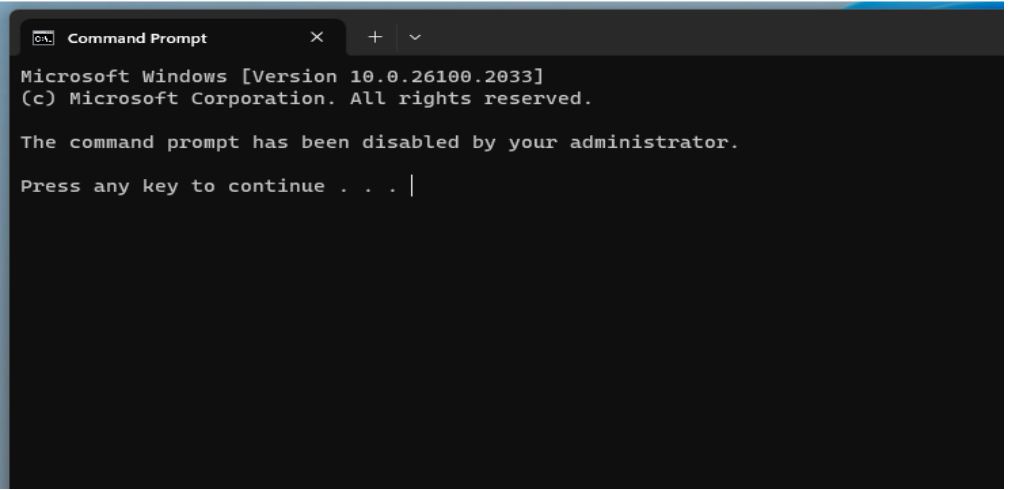
Purpose: Validates that the "LabUsers - Basic Restrictions" GPO is successfully applied to standard domain users and enforces intended security policies.
Post-Project Summary
Key Takeaways
- Active Directory is the backbone of Windows enterprise environments, providing centralized authentication and authorization services
- Proper planning and design of the OU structure is crucial for scalable and manageable Active Directory implementation
- DNS integration is critical for Active Directory functionality and must be properly configured and maintained
- Group Policy provides powerful centralized management capabilities but requires careful planning to avoid conflicts
- Security best practices should be implemented from the beginning, including proper delegation and least privilege principles
Troubleshooting Highlights
- Resolved DNS resolution issues that prevented successful domain controller promotion
- Addressed time synchronization problems between domain controller and client machines
- Fixed Group Policy application issues by understanding inheritance and precedence rules
- Troubleshot domain join failures related to network connectivity and DNS configuration
- Resolved authentication issues by verifying proper service account configurations
Next Steps
- Implement additional domain controllers for redundancy and load distribution
- Configure Active Directory Certificate Services for PKI implementation
- Set up Active Directory Federation Services for single sign-on capabilities
- Implement advanced security features such as Protected Users group and Authentication Policies
- Explore PowerShell automation for Active Directory management tasks
- Study Active Directory disaster recovery and backup strategies
Final Reflection
This Active Directory lab project provided comprehensive hands-on experience with enterprise directory services implementation. The project demonstrated the complexity and importance of proper planning in Active Directory deployments, from initial design through ongoing management.
The experience highlighted the interconnected nature of various Windows Server services and the critical role that Active Directory plays in modern IT infrastructure. Understanding these concepts is essential for any IT professional working in Windows-based enterprise environments.
Note: All IP addresses shown in this lab are from a private testing environment and are not publicly accessible.